Step right up and prepare to unravel the mysteries surrounding Pseudoscience vs mainstream science. Get ready for a mind-bending journey filled with intriguing facts and eye-opening revelations that will challenge your perception of what’s real and what’s not.
As we delve deeper into the realm of scientific exploration, you’ll discover the stark contrasts between legitimate scientific principles and the murky waters of pseudoscientific beliefs. Brace yourself for a rollercoaster ride of skepticism and discovery as we navigate this complex landscape together.
Pseudoscience vs Mainstream Science
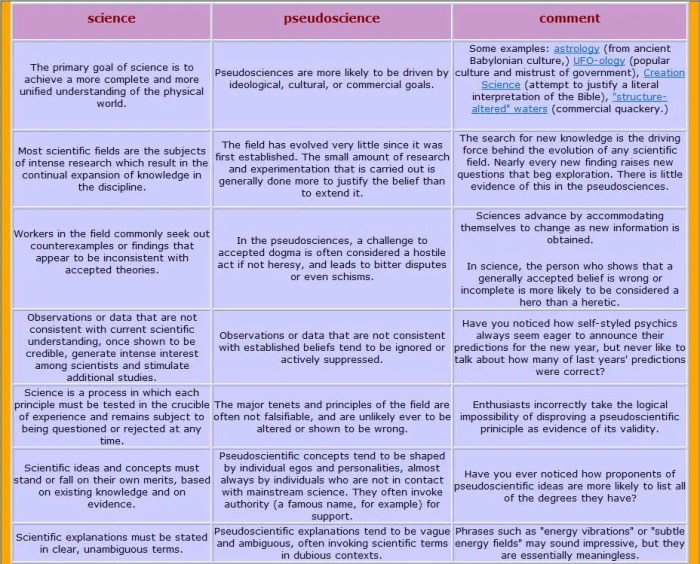
Pseudoscience and mainstream science are two distinct approaches to understanding the world around us. While mainstream science relies on empirical evidence, rigorous testing, and peer review to support its claims, pseudoscience often lacks scientific validity and is based on unproven theories or beliefs.
Fundamental Differences
- Mainstream science follows the scientific method, which involves making observations, forming hypotheses, conducting experiments, and drawing conclusions based on evidence. Pseudoscience, on the other hand, relies on anecdotal evidence, personal testimony, and unverified claims.
- Mainstream science is subject to peer review, where other experts in the field evaluate the validity of research before it is published. Pseudoscience often lacks peer-reviewed studies to support its claims.
- Mainstream science is constantly evolving based on new evidence and discoveries. Pseudoscience tends to cling to outdated ideas and beliefs even when evidence suggests otherwise.
Examples
- Mainstream Science: The theory of evolution, supported by extensive fossil records, genetic evidence, and observational data.
- Pseudoscience: Creationism, which posits that life on Earth was created by a divine being without scientific evidence to support this claim.
- Mainstream Science: Climate change, supported by data showing increasing global temperatures and the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Pseudoscience: Climate change denial, which rejects scientific consensus and relies on misinformation to downplay the severity of global warming.
Importance of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in distinguishing between pseudoscience and mainstream science. It allows individuals to evaluate evidence, question assumptions, and make informed decisions based on reliable information. By applying critical thinking skills, we can separate fact from fiction and avoid falling prey to pseudoscientific beliefs that lack empirical support.
Characteristics of Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience is characterized by several key aspects that differentiate it from mainstream scientific practices. One of the most significant differences lies in the lack of empirical evidence and adherence to scientific methodology.
Lack of Empirical Evidence
Pseudoscience often relies on anecdotal evidence, personal testimonials, or unverified claims to support its theories. This contrasts with mainstream science, which places a strong emphasis on empirical evidence obtained through systematic observation and experimentation. Without solid empirical evidence to back its claims, pseudoscience fails to meet the rigorous standards of scientific inquiry.
Absence of Scientific Methodology
In pseudoscience, the methodology used to investigate hypotheses is often flawed or non-existent. This can involve cherry-picking data, confirmation bias, or the use of faulty reasoning to arrive at predetermined conclusions. In contrast, mainstream science follows established scientific methods, such as formulating testable hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing results objectively.
Potential Dangers on Society and Individuals
Belief in pseudoscientific ideas can have harmful consequences for both society and individuals. When people accept pseudoscientific claims as truth without question, they may make decisions that jeopardize their health, safety, or financial well-being. In extreme cases, pseudoscience can lead to the spread of misinformation, fuel conspiracy theories, and undermine public trust in legitimate scientific research.
Characteristics of Mainstream Science
Mainstream science is characterized by a set of principles and methods that guide the research process, ensuring rigor and reliability in scientific investigations. In mainstream science, the focus is on following established protocols to gather evidence, test hypotheses, and draw conclusions based on empirical data.
Peer-Reviewed Studies
Peer-reviewed studies play a critical role in mainstream scientific research. These studies undergo rigorous evaluation by experts in the field before being published, ensuring the validity and quality of the research findings. Peer review helps to maintain high standards of accuracy and credibility in scientific publications.
- Mainstream science relies on peer-reviewed studies to validate research findings and establish a foundation of knowledge in various disciplines.
- Peer review helps to identify any flaws or biases in research methodologies, improving the overall quality of scientific publications.
- By submitting research to peer-reviewed journals, scientists contribute to the collective body of scientific knowledge and engage in a process of continuous improvement and refinement.
Experimentation and Empirical Evidence
Experimentation and empirical evidence are fundamental to mainstream scientific practices. Scientists design experiments to test hypotheses, gather data through observation and measurement, and use empirical evidence to support or refute their theories. This empirical approach ensures that scientific conclusions are based on objective evidence rather than speculation.
- In mainstream science, experiments are carefully designed to control variables, minimize bias, and produce reliable results that can be replicated by other researchers.
- Empirical evidence serves as the foundation for scientific theories, providing a basis for understanding natural phenomena and developing predictive models.
- Through experimentation and the systematic collection of data, scientists are able to make informed decisions, draw meaningful conclusions, and advance knowledge in their respective fields.
Skepticism and Openness to Revision
Skepticism and openness to revision are essential aspects of mainstream scientific practices. Scientists approach new ideas and hypotheses with a critical mindset, questioning assumptions and seeking evidence to support or challenge existing theories. This rigorous evaluation process promotes intellectual honesty and encourages continuous improvement in scientific understanding.
- Mainstream scientists are encouraged to be skeptical of claims that lack empirical support or contradict established scientific principles, promoting a culture of critical thinking and evidence-based reasoning.
- Openness to revision allows scientists to update their theories in response to new evidence, incorporating fresh perspectives and insights to enhance the accuracy and relevance of scientific knowledge.
- By embracing skepticism and remaining open to revision, mainstream science continually evolves, adapts, and expands our understanding of the natural world, driving innovation and discovery in diverse fields of research.
Impact on Society
Pseudoscience and mainstream science both have significant impacts on society, albeit in very different ways. Pseudoscience can influence public perception and decision-making by promoting false or unverified claims as legitimate scientific facts. This can lead to individuals making choices based on misinformation rather than evidence-based research, ultimately affecting their well-being and the community as a whole. On the other hand, promoting scientific literacy is crucial to combat the spread of pseudoscientific ideas and ensure that society makes informed decisions based on credible scientific findings.
Influence of Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience can have detrimental effects on society by spreading misinformation and promoting beliefs that are not supported by scientific evidence. For example, anti-vaccine movements based on pseudoscientific claims have led to a decline in vaccination rates, resulting in outbreaks of preventable diseases. This highlights the importance of critically evaluating information and understanding the difference between scientific facts and pseudoscientific claims.
Promoting Scientific Literacy
Educating the public about the principles of scientific inquiry and critical thinking is essential in combating the spread of pseudoscience. By promoting scientific literacy, individuals can better discern between credible scientific research and pseudoscientific claims, making informed decisions that benefit themselves and society as a whole. Scientific literacy also encourages a greater appreciation for the scientific method and the importance of evidence-based reasoning.
Impact of Mainstream Science
Mainstream science has positively impacted society through technological advancements and healthcare innovations. For instance, medical breakthroughs such as vaccines, antibiotics, and surgical procedures have significantly improved public health and increased life expectancy. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as the internet, telecommunications, and renewable energy sources, have transformed the way we live and communicate, leading to greater efficiency and connectivity in modern society.
Cooking and Culinary
Cooking is often seen as an art form where individuals can express creativity and personal flair in preparing dishes. On the other hand, culinary is more scientifically grounded, focusing on the precise techniques, measurements, and chemical reactions involved in food preparation.
Difference between Cooking as an Art and Culinary as a Science
- Cooking involves experimentation, creativity, and personal taste preferences, while culinary follows established scientific principles and techniques.
- Culinary professionals rely on precise measurements, temperature control, and understanding of chemical reactions to achieve consistent and high-quality results.
- Cooking can be spontaneous and flexible, allowing for improvisation, while culinary requires adherence to recipes and standardized procedures.
Chemical Reactions in Cooking and their Impact on Food
- When food is exposed to heat during cooking, chemical reactions such as the Maillard reaction occur, leading to the development of complex flavors and aromas.
- Acids in ingredients like citrus fruits can tenderize meat by breaking down proteins, while fats can enhance the richness and mouthfeel of dishes.
- Proper cooking techniques can maximize flavor extraction from ingredients, transforming raw components into delicious and palatable dishes.
Importance of Proper Food Handling, Storage, and Preparation Techniques
- Proper food handling practices are crucial to prevent contamination and foodborne illnesses, ensuring the safety of consumers.
- Correct storage techniques help maintain the freshness and quality of ingredients, preserving their nutritional value and taste.
- Adhering to precise preparation techniques in culinary practices ensures consistency in results and meets quality standards expected in professional kitchens.
Cultural Influences
Food is not just about sustenance; it is deeply intertwined with culture, traditions, and social interactions. Different cultures around the world have unique culinary traditions that have been shaped by history, geography, and societal norms.
Globalization of Food
The globalization of food has led to a blending of culinary traditions from different parts of the world. This has resulted in a diverse range of cuisines available in various countries, with people being able to enjoy dishes from different cultures without leaving their own neighborhoods.
Role of Food in Cultural Celebrations
Food plays a significant role in cultural celebrations and rituals. Many cultures have specific foods that are prepared during festivals, weddings, and other important events. These dishes often have symbolic meanings and are meant to bring good luck or prosperity.
Social Gatherings
Food also plays a central role in social gatherings, whether it’s a family dinner, a potluck with friends, or a community feast. Sharing a meal brings people together, fosters relationships, and creates a sense of community.
Health and Nutrition
Cooking methods and food choices play a crucial role in determining our overall health. The way we prepare our meals can impact the nutritional content of the food we consume, which in turn affects our well-being. It is essential to understand the relationship between culinary practices and their influence on our dietary habits to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Importance of Balanced Nutrition
Having a balanced diet is key to promoting good health and preventing diseases. It involves consuming the right proportion of nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. By incorporating a variety of foods in our meals, we ensure that our bodies receive the necessary nutrients to function optimally.
- Include a colorful array of fruits and vegetables in your meals to ensure you get a wide range of vitamins and minerals.
- Opt for whole grains over refined grains to increase fiber intake and promote digestive health.
- Choose lean sources of protein, such as poultry, fish, beans, and legumes, to reduce saturated fat consumption.
- Limit the intake of processed foods high in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats to maintain a healthy weight and lower the risk of chronic conditions.
Culinary Practices and Dietary Habits
The way we prepare and cook our food can significantly impact our dietary habits. By being mindful of cooking methods and ingredient choices, we can create nutritious and delicious meals that support our well-being.
- Opt for steaming, baking, grilling, or sautéing instead of deep-frying to reduce the amount of added fats and calories in your dishes.
- Experiment with herbs, spices, and citrus juices to enhance the flavor of your meals without relying on excessive salt or sugar.
- Incorporate a variety of plant-based proteins, such as tofu, tempeh, and lentils, into your diet to reduce the consumption of animal products and promote heart health.
- Practice mindful eating by savoring each bite, listening to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, and avoiding distractions during meals to prevent overeating.
Ultimate Conclusion
In a world where truth and fiction often blur, it’s crucial to equip ourselves with the tools of critical thinking and scientific reasoning. As we bid adieu to this enlightening discussion on Pseudoscience vs mainstream science, remember to question, probe, and always seek the truth behind the curtain of scientific claims.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the main difference between pseudoscience and mainstream science?
Pseudoscience relies on unproven claims and lacks empirical evidence, while mainstream science follows rigorous scientific methods and peer-reviewed research.
How can pseudoscientific beliefs impact society?
Pseudoscientific ideas can mislead the public, influence decision-making, and potentially harm individuals who rely on unfounded claims.
What role does skepticism play in mainstream scientific practices?
Skepticism is essential in science to question hypotheses, validate results, and ensure the credibility of scientific findings through rigorous scrutiny.